Top 10 Facts about the Great Wall
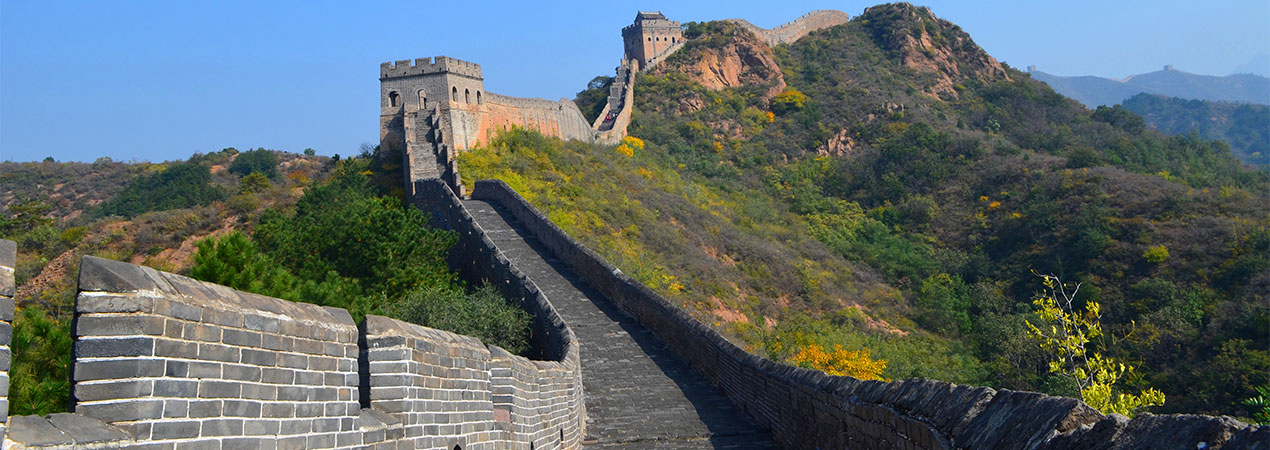

The Great Wall of China, listed as a World Heritage Site by UNESCO in 1987, is a representation of the collective skill and cleverness of ancient Chinese people. As one of the greatest wonders in the world, The Great Wall stretches for 13,049 miles through 15 provinces from east to west of China. The first part of the Wall was built more than 2,000 years ago. The construction lasted until the Ming Dynasty (1368AD-1644AD). Travel with us to the various sections of the Wall, from the wild sections to the well-preserved ones, to admire its magnificent architecture and historical connotation.
1. Where is the starting point of the Great Wall?
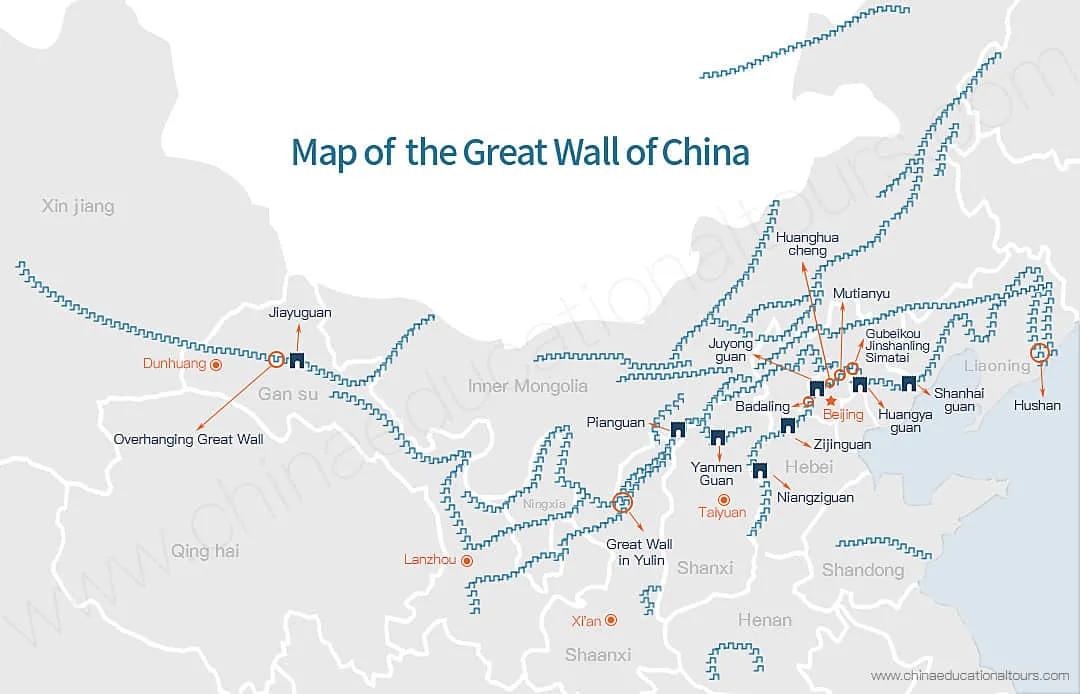
The majority of people think that the Great Wall begins in the east at the Shanhaiguan Pass and ends at the Jiayuguan Pass in the west. But actually it was confirmed by an archaeologist in 1992 that it starts from a point east of Hushan Mountain in Liaoning Province that is located next to the Yalu River. This archaeological discovery has also been proved to be true in the history books.
2. What is the Great Wall for?
 Watch Tower on the Great Wall
Watch Tower on the Great Wall
The Great Wall was originally used for defense from disturbances as well as being intended to enclose the city. In fact, parts of the Great Wall were built for protection against disturbances after the Warring States period (about 475 to 221 BCE) and the unification by the first emperor of the Qin Dynasty. Later other dynasties also built more parts as a safeguard against incursions by the dominator of the Central Plain. However, in addition to this, protecting communication and traveling for business were also vital functions of the Great Wall. During the period of the first emperor of the Qin Dynasty, along the 12 prefectures of the Great Wall, there were avenues for communication with each other, for the delivery of writs and business contacts and journeys. The Great Wall and the beacon towers were what made the traffic run freely. During the Han Dynasty when a road was constructed right through to the Western Region, this avenue was still used for frequent contact with envoys and for business trips. The Great Wall and the beacon towers were built alongside this avenue, in order to protect the road known as the Silk Road.
3. Who built the Great Wall?

In the past, people thought that the Great Wall was built for defending China from ethnic minorities, but this was really a misunderstanding. Actually, if we put aside the construction by principalities of pre-Qin (who built large parts of the Great Wall), after the first emperor of the Qin Dynasty there were also three dynasties unified by Han nationality. These were Han, Sui and Ming. But there were also five dynasties unified by ethnic minorities which had built the Great Wall, and these were North Wei, North Qi, North Zhou, Liao and Jin. Consequently, the Great Wall was the accumulation of wisdom and hard work from people of all minorities.
4. How long did it take to build the Great Wall? and How long is the Great Wall?
Beginning in the 7th or 8th century BCE, the Great Wall was built over a period of 2000 years, distributed among the extensive land of northern and central China, and with a total length of more than 80000 kilometers. The part of the Ming Great Wall which was better preserved stretched for over 2000 km.
5. Is the Great Wall visible from the Space Station?
It has been proved to be untrue that the Great Wall was the only man-made building that can be seen from the space station. The Great Wall is six meters in width and it cannot be seen with the naked eye even from a height of 20km(which is twice the normal flight altitude). Even though its shadow can make it appear bigger, the altitude at which the Great Wall disappears into the background and vanishes completely is only 60km. Such an altitude is way below the 300-400 km of the minimum regular orbit of a satellite or a space shuttle.
6. Which parts of the ancient Great Wall are the best preserved?
Some say that the ancient Great Wall of the Ming Dynasty (which is located in Wulong Ditch in Laiyuan County of Hebei Province) was the best preserved section. Others say that the pretty Inner Mongolia province keeps the longest and best site of the ancient Great Wall. Also among the best is Baotou city which keeps the most integrated section of the Great Wall of the Zhao Dynasty. In Xiaoshetai County, Urad Front Banner, Bayan Nur City and inside the Guyang County of Baotou City, there are other well integrated parts of the Qin Great Wall. The ancient Great Wall along the inside of Xilin Gol League was built during the period of Qin, Yan and Jin, and most of it was made with earth and stone. The Qin Great Wall distributed in the south hilly area of Xilin Gol League, stretching through the difficult terrain, was mostly made with earth and stone, and had barriers. The Yan Great Wall distributed in the Duolun County, West Ujimqin Banner, and the inner part of the Abaga Banner, winds for thousands of miles.
7. Why hasn’t the Great Wall fallen down?
 Simatai Great Wall
Simatai Great Wall
It was reported in the foreign media that the latest research shows that delicious sticky rice - which has become a major part of Asian people’s diet -was also what made the ancient Chinese mortar cement so strong. The researchers also found that such mortar is still the best existing material for repairing the ancient wall.
Mortar is a paste that is used to fill the cracks between bricks, stones and other building materials. Zhang Bingjian (transliteration), a Chinese scientist, and his colleagues found that the ancient Chinese building workers invented the high-strength sticky rice mortar through mixing the sticky rice and normal mortar about 1500 years ago.
Sticky rice mortar may be the first compound mortar that was made with organic and inorganic materials in the world. Sticky rice mortar has greater strength and be more waterproof than unmixed lime mortar. Building workers used the sticky rice mortar to repair graves, pagodas and ramparts, and some of the buildings they repaired still exist. Some buildings were so firm that they couldn’t even be knocked down with a modern bulldozer. They can also withstand high-strength earthquakes.
8. How many state leaders have climbed the Great Wall?
Over 480 Heads of State have climbed the Great Wall. Here are some of the most well-known:
 The Great Wall of China
The Great Wall of China
- Queen Elizabeth Ⅱ, 14.10.1986.
- Spanish Prime Minister, Jose Maria Aznar, 26.6.2000.
- US President Richard Nixon, 24.2.1972.
- US President Ronald Reagan, 28.4.1984.
- US President Barack Obama, 18.11.2009.
- Japanese Prime Minister, Kakuei Tanaka, 27.9.1972.
- Britain's Prime Minister, David Cameron, 10.11.2010
- Russian President Vladimir Putin, 3.12.2002.
- Russian President Yeltsin, 17.12.1992.
9. What was the cost in manpower and resources for building the Great Wall?
Let’s take the first emperor of the Qin dynasty as an example. The first emperor of the Qin dynasty decided to build the Great Wall after unifying China. The senior general, Meng Tian, was designated for the command and ordered 300 thousand workers to successively link the north ramparts to that of the previous county like Yan, Zhao, Qin and so on within about 10 years. So the Great Wall with the length of thousands of miles was formed, which begins in the west from the Lintao county (now Minxian County) of Gansu Province and ends at the Liaodong Peninsula in the east.
10. How did the Great Wall defend the country?
There are three military functions of the Great Wall: early-warning, transportation, and maintenance for the front.
Early-warning:
The Great Wall was not a solitary Great Wall, there were also a series of strongholds apart from it. These were what played the role of an early-warning diversionary function. The more powerful the dynasty was, the more strongholds they owned. When a dynasty was relatively weak, it owned less strongholds.
Maintenance for the front:
Behind the Great Wall there were a series of logistics supply points and military depots of the vital areas. These could ensure the battle effectiveness of troops with enough supplies no matter how long the front was.
Transportation:
While the nomads outside the Great Wall attacked the Central Plains Dynasty, they had to cross the mountains and spend a lot of time as well as manpower. It was very difficult for them to move their war materials. However, the existence of the Great Wall meant the central army with less climbing ability found it easier to march and transport their goods on the ground than the nomads, so that they could save physical exertion for fighting.
Continue reading: Top 10 Great Wall Sections
Drop us a line and we'll connect you with the top China expert in no time!
